8
2014 Year in Review
2014 was an exciting year for the Space and Satellite sector marked by expanding competition,
ambitious investments and headline successes – among the most notable of which was the
successful landing of the Rosetta Mission’s Philae Probe on a comet.
Launch Sector Competition:
Although the launch sector has experienced few significant
technological changes as of late, the federal funding mechanisms are rapidly evolving. Since
governments typically sponsor two-thirds or more of annual launches, this is quickly reshaping
the competitive landscape. Launch contracts are shifting from traditional government
contracting vehicles to less stringent contracts allowing contractors greater discretion in
exchange for cost reductions. This shift has made room for commercial players such as
SpaceX to grab market share from Boeing and Lockheed’s United Launch Alliance (ULA), the
long-dominant industry prime. SpaceX has already completed 14 successful launches, won a
$1.6 billion NASA contract to resupply the International Space Station and captured a $2.6
billion contract to design the next-generation NASA transport system. Additionally, SpaceX is
now protesting the Air Force $11.0 Billion Evolved Expendable Launch Vehicle award to ULA
and most recently received a $1.0 billion investment from Google. The shifting contracting
landscape is part of the strategic rationale behind the planned $5.0 billion Orbital Sciences and
ATK Aerospace and Defense Group merger. The deal has progressed despite an October
launch failure as the two companies look to leverage their combined reputations and
capabilities to capitalize on the evolving marketplace and opportunities for innovation.
Satellite Market Disruptors:
Innovations in satellite technology and rapidly growing demand
from TV and Internet providers are helping fuel commercial launch demand. However, Google’s
foray into the satellite market via its $500 million purchase of Skybox presents several areas of
potential market disruption. Google’s model of adding internet users to drive advertising
revenue is an interesting challenge to traditional satellite revenue streams based on fee for
service. Additionally, existing fixed cost models are being impacted by satellite size reductions
through Cubesat design and other innovations. Skybox satellites are 20x smaller, 10x cheaper
than traditional satellites and visual acuity is generated from its software rather than optics.
Further, frameworks are increasingly based on open source technologies. These innovations
are lowering costs by allowing multiple satellites a single launch vehicle and limiting
maintenance and upgrades, creating new opportunities for both consumers and suppliers.
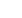
Market Evolution in Space and Satellite
Source: Open Sources, Public Filings, “Sate of the Satellite Industry Report 2014” The Tauri Group
Notable Space & Satellite Acquisitions
Aerospace & Defense
Cubesat Launches
91
140
0
20
40
60
80
100
120
140
160
Cubesat Unit Cost Scale
Low Cost:
1U cubesat bus kits $13,000, with 6U
configurations reaching $30,000
Moderate Cost:
Boeing-built cubesat platforms for
NRO are estimated at $250,000
Higher Cost:
NASA estimates cubesats used for
planetary science missions at $3-$10 million
Space Operations
Space Photovoltaics
acquired
acquired
will merge
acquired
acquired