3
Second Quarter 2015
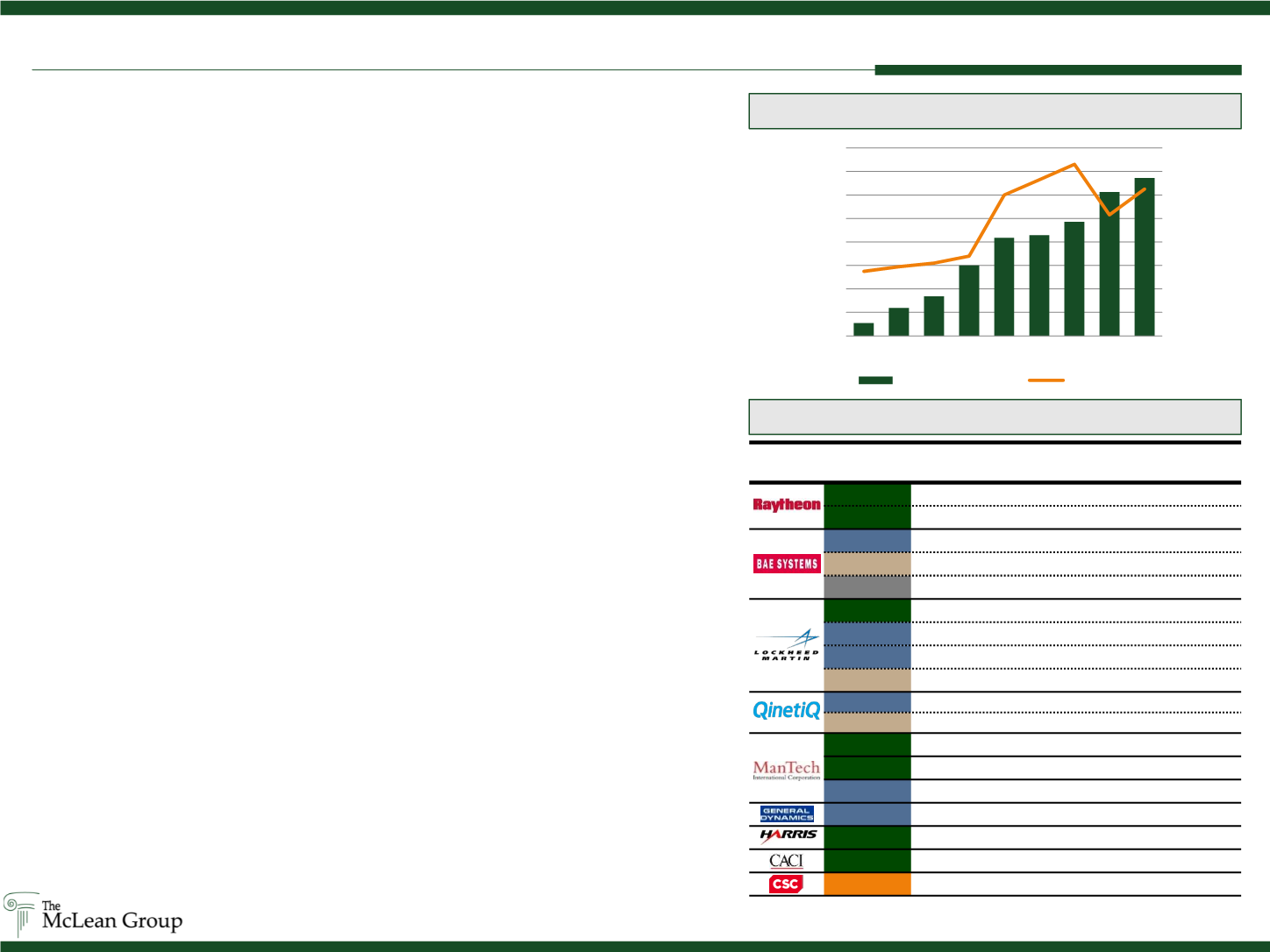
Company
Strategic Actions
Sector
Value /
Size
Acquired
Blackbird
Cybersecurity / A&D $420M EV
Acquired
Websense
Cybersecurity
$1.7B EV
Will Divest
IC Solutions Div.
Gov. Services & IT
$1.7B Rev
Will Retain
Applied Intell.
Cybersecurity
NA
Reinvesting in
Land Systems
A&D
NA
Will Acquire
Sikorsky
A&D
$9.0B EV
Will Divest
IS&GS
Gov. Services & IT
$6B Rev
Will Divest
Commercial Cyber
Commercial Cyber
NA
Will Retain
Gov. Cybersecurity Gov. Cybersecurity
NA
Divested
QinetiQ N.A.
Gov. Services & IT
$780M Rev
Retained
Cyveillance
Cybersecurity
$20M Rev
Acquired
STG
Gov. Cybersecurity
$166M EV
Acquired
KSG
Cybersecurity
NA
Divested
MCSI
Commercial Cyber
NA
Divested
Fidelis
Commercial Cyber
NA
Acquired
Exelis
A&D
$4.7B
Acquired
LTC Engineering
Cybersecurity
$16M
Split
Dividing into US Public Sector and Global Commercial
Cyber Security and IT M&A Trends
Source: OMB Annual Reports to Congress: FISMA
1
, OPM Office of Communicaitons
2
; S&P Capital IQ; DACIS, Wired
Large Prime Contractor Portfolio Restructuring
$0
$2
$4
$6
$8
$10
$12
$14
$16
0
10,000
20,000
30,000
40,000
50,000
60,000
70,000
80,000
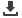
2006 2007 2008 2009 2010 2011 2012 2013 2014
FISMA Spending (Billions)
Number of Incidents (Thousands)
Reported Incidents
FISMA Spending
Reported FISMA Security Incidents and Spending
2
In May the Office of Personnel Management (OPM) announced that it was hacked by foreign
agents, exposing the personal information of more than 21 million federal employee and
applicant files.
1
This is only the latest of many recent federal data breaches – NSA, IRS,
USPS, Healthcare.gov – and further highlights government IT infrastructure vulnerabilities as
the number of reported cyber security incidents climb.
2
Consequently, IT and cybersecurity
modernization is a rapidly growing federal priority. Agencies hope not only to modernize the
systems, but also cut costs, especially in traditional IT services. Cost savings are expected to
free up funds for specialized services such as cybersecurity and advanced analytics.
Additional strategic priority shifts are driven by the Defense Department’s light footprint
strategy which relies heavily on superior defense and communications systems. The new
strategy’s technical demands are motivating contractors to realign core capabilities focusing
on these systems’ requirements which will provide greater long-term growth and margins.
M&A activity shows large prime contractors already executing on this strategy, building
capabilities in cyber and defense systems while exiting the more traditional IT and
professional services. The largest acquisition representing this trend is Harris Corp’s
purchase of Exelis for $4.7 billion. Completed in May, Exelis provides Harris with significant
synergy opportunities, especially across C4ISR. Raytheon’s purchases of Blackbird
Technologies for $420 million and Websense for $1.7 billion exemplify a cyber security focus.
In April, BAE announced plans to divest large parts of its Intelligence Community services
business, using the proceeds to develop aerospace and defense products. BAE will retain its
cybersecurity arm and Systems Applied Intelligence. Shortly after Q2 close, Lockheed Martin
disclosed similar plans, announcing its intention to acquire Sikorsky for $9 billion while
exploring sale options for its Information Systems & Global Solutions (IS&GS) division, but
retaining its specialized cybersecurity capabilities.
Converse to Raytheon’s foray into commercial cyber with its purchase of Websense,
Lockheed intends to exit its commercial cyber position. A move proceeded by both General
Dynamics and ManTech which divested commercial cybersecurity positions in Q2. Despite
synergy potential, commercial and public sector cybersecurity capabilities prove difficult to
integrate, causing contractors to refine focus on public sector cyber. Both ManTech and
CACI demonstrated this in Q2 with public sector cybersecurity acquisitions. Also indicative of
this challenge is CSC’s announced split which will result in two publicly traded companies,
one focused on Global Commercial customers and the other on the US Public Sector.
Going forward prime contractors will likely focus on further refining portfolios to stay ahead of
specific government technology and cyber security modernization and acquisition priorities.
Further divestitures are expected along with targeted mid-market acquisitions of small, high
margin companies offering specialized services and capabilities.